chondrocytes|chondrocyte vs chondroblast : Pilipinas The cartilage is solely composed of cells known as chondrocytes. Chondrocytes maintain the extracellular matrix (ECM) . Portal Do Cliente - Expresso São Miguel
0 · what do chondrocytes look like
1 · what are chondrocytes called
2 · chondrocytes wikipedia
3 · chondrocytes function anatomy
4 · chondrocytes are found in
5 · chondrocytes are cells found in
6 · chondrocyte vs chondroblast
7 · chondrocyte meaning
8 · More
WEBUse o Google Slides para criar apresentações de diapositivos online. Crie apresentações apelativas em modo de colaboração, com partilha segura em tempo real e a partir de .
chondrocytes*******The cartilage is solely composed of cells known as chondrocytes. Chondrocytes maintain the extracellular matrix (ECM) . Chondrocytes are the cells that produce collagen and the extracellular matrix of cartilage. Learn about the three types of cartilage, the process of .chondrocytesChondrocytes are metabolically active cells that synthesize and turnover a large volume of extra cellular matrix (ECM) components such as collagen, glycoproteins, proteoglycans, .Learn about chondrocytes, the only cell type in mature cartilage tissue, and their roles in endochondral bone formation and growth plate development. Find chapters and . Sox9 Can Maintain Chondrocytes Phenotype and Inhibit Chondrocyte Hypertrophy. SRY-box 9 protein (Sox9) is an important transcription factor that mediates .In this Review, Thomas Aigner and colleagues discuss the pivotal role of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis. The article focuses on changes in the anabolic, catabolic, phenotypic and proliferative . As a small number of cells was used to examine the transcriptomes of P0–8 chondrocytes, the results were compared with previously published scRNA-seq data .
The cartilage is solely composed of cells known as chondrocytes. Chondrocytes maintain the extracellular matrix (ECM) and produce the cartilage matrix. . Chondrocytes begin to express RUNX2, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), collagen X, and MMP-13 [28,29]. This is a shift towards hypertrophy, followed .In this Review, Thomas Aigner and colleagues discuss the pivotal role of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis. The article focuses on changes in the anabolic, catabolic, phenotypic and proliferative .
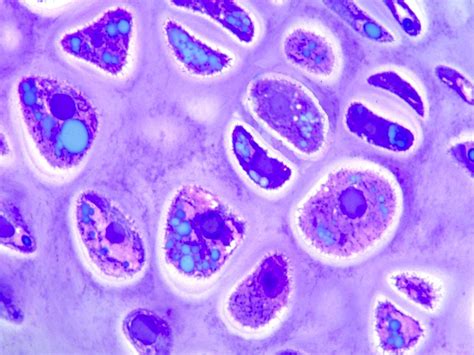
Even a study as early as 1992 in chick embryos suggested that hypertrophic chondrocytes have the capability to transdifferentiate into bone-matrix-forming cells. 55 Consistent with this data, we .
Traumatic joint injuries often result in elevated proinflammatory cytokine (such as IL-1β) levels in the joint cavity, which can increase the catabolic activities of chondrocytes and damage . The cartilage is solely composed of cells known as chondrocytes. Chondrocytes maintain the extracellular matrix (ECM) and produce the cartilage matrix. Surrounded by collagenous fibers, chondrocytes release substances to make cartilage strong yet flexible. In general, chondrocytes are found within intervertebral discs and in .Other articles where chondrocyte is discussed: connective tissue: Cartilage: The cells of cartilage, called chondrocytes, are isolated in small lacunae within the matrix. Although cartilage is avascular, gaseous metabolites and nutrients can diffuse through the aqueous phase of the gel-like matrix to reach the cells. Cartilage is enclosed by the .
Growth plate chondrocytes play central roles in the proper development and growth of endochondral bones. Particularly, a population of chondrocytes in the resting zone expressing parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) is now recognized as skeletal stem cells, defined by their ability to undergo self-renewal and clonally give rise .
Chondrocytes begin to express RUNX2, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), collagen X, and MMP-13 [28,29]. This is a shift towards hypertrophy, followed by the calcification of the ECM around chondrocytes and subchondral bone sclerosis. These changes in both cartilage and bone occur before the onset of clinical symptoms.
Mechanosensors of chondrocytes and their roles in OA pathogenesis. Mechanosensors respond to mechanical stimulation that alter the molecular/cellular structures to induce electrochemical and .

40.2.3 Chondrocytes. Chondrocytes are the cells responsible for cartilage formation, and they are crucial for the process of endochondral ossification, which is useful for bone development. Also, by mimicking skeletal development chondrocytes play a critical role in fracture repair. Chondral cells derive from the same multipotential mesenchymal .
Articular chondrocytes are exclusively responsible for the turnover of the extracellular matrix (ECM) of hyaline cartilage. However, chondrocytes are phenotypically unstable and, if they de-differentiate into hypertrophic or fibroblastic forms, will produce a defective and weak matrix. Chondrocyte volume and morphology exert a strong influence . Articular cartilage (AC) covers the diarthrodial joints and is responsible for the mechanical distribution of loads across the joints. The majority of its structure and function is controlled by chondrocytes that regulate Extracellular Matrix (ECM) turnover and maintain tissue homeostasis. Imbalance in their function leads to degenerative diseases like .Articular chondrocytes are cells responsible for the unique features of articular cartilage; therefore, it would appear appropriate to use true committed chondrocytes to engineer in vitro or in vivo cartilage to repair a cartilaginous defect. Human articular chondrocytes derived from articular cartilage biopsies have a limited proliferative potential that declines . Chondrocytes are specialized types of cells that are responsible for forming, and are only found in, cartilage. Cartilage is a soft, firm, flexible, and resilient connective tissue that serves as . Chondrocytes are the key target cells of the cartilage degeneration that occurs in Kashin–Beck disease (KBD) and osteoarthritis (OA). However, the heterogeneity of articular cartilage cell types .chondrocytes chondrocyte vs chondroblast Chondrocytes maintain the extracellular matrix (ECM) and produce the cartilage matrix. Surrounded by collagenous fibers, chondrocytes release substances to make cartilage strong yet flexible. In general, chondrocytes are found within intervertebral discs and in any form of articular cartilage (AC).Chondrocytes recognize the loss of ECM and actively produce collagen type II and proteoglycans. However, the ratio between the ECM protein production to proteolytic enzyme production is imbalanced and results in complete loss .
Chondrocytes are the primary cells found in the extracellular matrix of cartilage. Learn more here at Kenhub!Chondrocytes are highly specialized cells that differentiate from clusters of mesenchymal cells during skeletal embryogenesis. The chondrocyte synthesizes and secretes the components of the extracellular matrix, primarily proteoglycans and type II collagen.Chondrocytes, which comprise the only cellular component of articular cartilage, have different morphologies ranging from more flattened at the surface to rounder and larger in the deeper zones. The cartilage is solely composed of cells known as chondrocytes. Chondrocytes maintain the extracellular matrix (ECM) and produce the cartilage matrix. Surrounded by collagenous fibers, chondrocytes release substances to make cartilage strong yet flexible.
chondrocyte vs chondroblastChondrocyte is a unique cell type in articular cartilage tissue and is essential for cartilage formation and functionality. It arises from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and is regulated by a series of cytokine and transcription factor interactions, including the transforming growth factor-beta super ..Following chondrogenesis, the chondrocytes remain as resting cells to form the articular cartilage or undergo proliferation, terminal differentiation to chondrocyte hypertrophy, and apoptosis in a process termed endochondral ossification, whereby the hypertrophic cartilage is replaced by bone.
21 linhas · Learn how to make various features and effects for RPG Maker VX Ace, such as items, events, monsters, puzzles, animations, and more. Browse the latest tutorials from .
chondrocytes|chondrocyte vs chondroblast